One of the treatments used to treat a retinal detachment, pneumatic retinopexy is an office-based procedure involving injection of a gas bubble into the eye to gently push the retina back into place along with application of a laser (photocoagulation) or freezing therapy (cryopexy) to seal off the area around it.
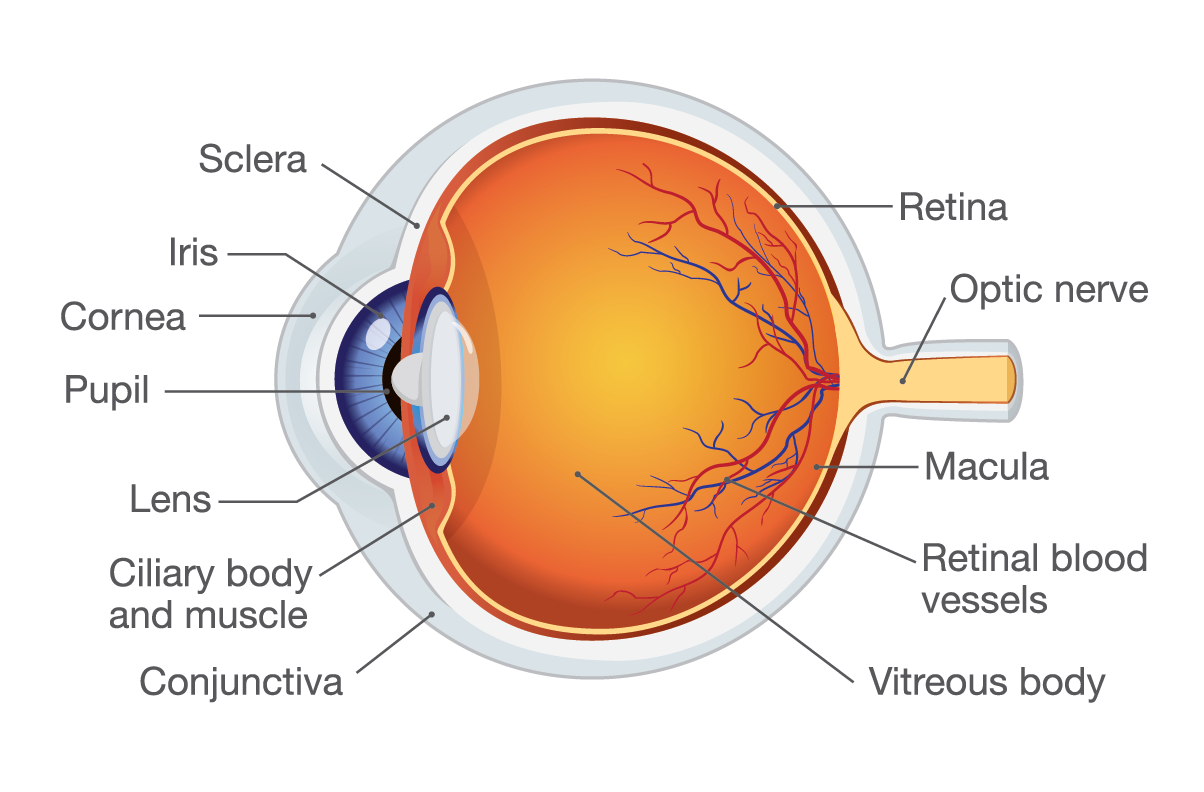
A retinal detachment occurs when fluid gets under the retina, usually through a retinal tear, and lifts part or all of it away from the back of the eye, causing it to no longer work right and your vision to become blurry. If left untreated, it almost always leads to blindness. If you have a retinal detachment, pneumatic retinopexy can prevent further retinal damage and may save your remaining sight.
Pneumatic retinopexy is performed for certain types of retinal detachments. These can include:
- When one retinal tear has caused the detachment
- When multiple small tears are close together
- When the tear is in the upper part of the retina
What to Expect
An outpatient procedure, pneumatic retinopexy begins by applying anesthesia in and around your eye to minimize discomfort. Your Texas Retina Associates surgeon will then inject a gas bubble in the middle of your eye and position your head to allow the bubble to float to the detached area of the retina and flatten it. Next, your surgeon will seal off the area around it using either a laser (photocoagulation) or freezing therapy (cryopexy). This may take place immediately after injecting the gas bubble or a few days later, depending on your specific condition.
After Pneumatic Retinopexy
Plan to have someone drive you home after your pneumatic retinopexy procedure. Your doctor may tell you to keep your head in a certain position for a determined length of time to allow the gas bubble to hold the retina in place properly and foster healing. The eye’s natural fluid will eventually replace the gas bubble.
You will need to avoid air travel while the gas bubble is in your eye. A change in altitude or air pressure can cause a gas bubble to expand and elevate intraocular pressure in the eye. This can result in severe eye pain and may lead to permanent loss of sight.
Call your physician if you notice any of the following after your pneumatic retinopexy procedure:
- Decreasing vision
- Increased pain
- Increased redness in the eye
- Swelling around the eye
- Discharge from the eye
- Any new floaters or flashes of light in your field of vision
Other treatments for retinal detachment include vitrectomy and scleral buckle surgery. Your Texas Retina Associates surgeon will determine the best treatment option to help preserve your vision.
Click here to watch a video about pneumatic retinopexy treatment for retinal detachment.